Abstract
Background:
Salvage options for patients with relapsed T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) are limited, with less than 25% of these patients achieving second remission 1, 2. 70% of T-ALL cases have activating mutations of the NOTCH1 pathway, which transcriptionally activates MYC by binding to its `superenhancer' region 3, 4. Other deregulated oncogenic pathways in T-ALL include PI3K/Akt, the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family, and CDKN2A/2B cell cycle regulators 5, 6. The NOTCH1-MYC regulatory circuit is an attractive therapeutic target, but clinical development of gamma-secretase inhibitors (GSI) to target NOTCH1 has been limited by 'on target' toxicities. A better target may be BRD4, a critical component of superenhancer complexes that binds to acetylated histone (3 and 4) and drives NOTCH1 mediated MYC transcription7.
ARV-825 is a hetero-bifunctional PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera (PROTAC) that has 3 components: a thienodiazepine-based BRD4 ligand, a linker arm, and a cereblon-binding ligand. ARV-825 recruits BRD4 to the E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon and leads to efficient and sustained degradation of BRD4, resulting in down-regulation of MYC.
Methods: We investigated the effectiveness of ARV-825 against T-ALL cell lines, including GSI-resistant lines. Since microenvironmental signals are critical for the survival of T-ALL, we specifically tested the impact of BRD4 degradation on CD44/CD44v, which integrates cell-extrinsic microenvironmental signals and is part of cysteine transporter that maintains low intra-cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), necessary for T-ALL survival and the persistence of disease. We also examined the anti-leukemic effect of ARV-825 in a T-ALL patient-derived xenograft (PDX) mouse model of disseminated leukemia with a constitutively active NOTCH1 mutation.
Results: The IC50s for all tested T-ALL cell lines at 72 hours were in the low nanomolar range (< 50 nM). ARV-825 leads to sustained degradation of BRD4 and down-regulation of its transcriptional targets MYC, Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in GSI-sensitive (HPB-ALL, KOPT1) and GSI-resistant (MOLT4, SUPT1) cell lines.
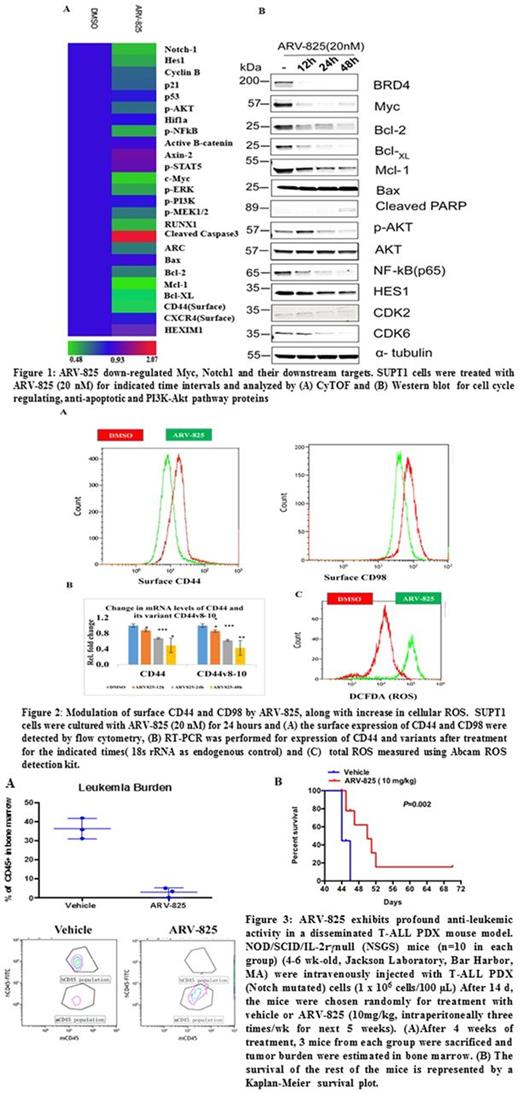
Mass cytometry based proteomic analysis (CyTOF) and immunoblotting showed that ARV-825 down-regulated cell intrinsic oncogenic molecules: transcription factors Myc and NFkB, cell cycle regulator CDK6, activated PI3K/Akt, and anti-apoptotic Bcl2 family proteins. In addition ARV-825 down regulated two key molecules involved in leukemia-stroma interaction; CD44 (Fig. 1), and CD98, a component of amino acid transporters xCT, LAT1 and 2, both essential in regulation of oxidative stress. Quantitative PCR and immunoblotting analysis confirmed the transcriptional down regulation of total CD44 and CD44 variants 8-10 (2-fold change treated vs . untreated). As a functional correlate of down-regulation of CD98/CD44/CD44v, flow cytometry confirmed increased intracellular ROS generation (Fig. 2).
Finally, in a PDX mouse model of human T-ALL, ARV-825 treatment resulted in lower leukemia burden (confirmed by flow cytometry for human CD45+ cells in bone marrow) and better survival compared to vehicle-treated control mice (p=0.002) (Fig.3).
Reference:
1. Marks DI, Rowntree C. Management of adults with T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017; 129(9): 1134-1142.
2. Litzow MR, Ferrando AA. How I treat T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. Blood 2015; 126(7): 833-41.
3. Sanchez-Martin M, Ferrando A. The NOTCH1-MYC highway toward T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2017; 129(9): 1124-1133.
4. Demarest RM, Ratti F, Capobianco AJ. It's T-ALL about Notch. Oncogene 2008; 27(38): 5082-91.
5. Girardi T, Vicente C, Cools J, De Keersmaecker K. The genetics and molecular biology of T-ALL. Blood 2017; 129(9): 1113-1123.
6. Joshi I, Minter LM, Telfer J, Demarest RM, Capobianco AJ, Aster JC et al. Notch signaling mediates G1/S cell-cycle progression in T cells via cyclin D3 and its dependent kinases. Blood 2009; 113(8): 1689-98.
7. Loven J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, Lau A, Orlando DA, Vakoc CR et al. Selective inhibition of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell 2013; 153(2): 320-34.
Qian: 4Arvinas, LLC. New Haven, CT: Employment. Raina: 4Arvinas, LLC. New Haven, CT: Employment. McKay: 6 ImmunoGen, Inc.Waltham, MA: Employment. Kantarjian: Novartis: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding. Andreeff: Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.